PSD2: what is it and why does it matter?
The Payment Services Directive (PSD2) is the new EU financial directive. It obliges banks to open up their data in a secured form so that it can be conveniently moved and shared between authorized Third Party Providers (TPPs).
Opening up banking data might not sound like much, but it could very much change the way we manage money.
The main objective of PSD2 is to create a safe open-banking environment, encouraging innovation and market efficiency in the Single Euro Payments Area.
The revised PSD2 directive will go into effect on the 14th of September 2019, and it will shake up the banking world as we know it.
How PSD2 is different from the original Payment Service Directive?
The existing Payment Service Directive was designed back in 2007 with three main objectives in mind:
To regulate payment services
To improve the quality of financial services.
To better protect consumers and promote competition.
Even though PSD2 stays true to that original mission, there are some major differences between the two.
The original PSD applied only to payments within the Single Euro Payments Area. Unlike its predecessor, PSD2 enables so-called "one-leg-out transactions." Under the PSD2, payments in any currency can be processed, as long as at least one payment service provider is located inside the EU.
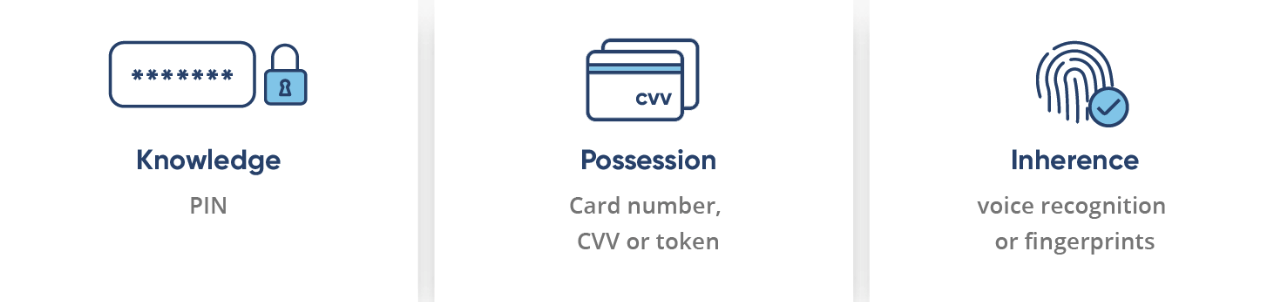
PSD2 also has introduced minimum requirements for Strong Customer Authentication. Under the revised Directive, users will have to go through two or more independent authentication levels:
But the most significant difference between the two is the introduction of Third Party Providers concept. The concept of TPP opens a whole new market for innovation in both the ecommerce and fintech market.
Third-party account access
Opening up banking data will significantly smoothen customer experience.
Instead of going through various intermediaries (like payment gateways and credit card networks), customers will be able to pay directly from their bank account, without involving other organizations.
Under the PSD2, there are two types of Third-Party Players that bank accounts can open to Account Information Service Providers (AISPs) and Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs).
Account Information Service Providers (AISPs) are providers authorized to access account data provided by banks.
Typical examples of AISP applications are Money Management and Budgeting Tools. These personal finance apps bring together data from different accounts and provide user's complete financial picture in one place.
Online loan application apps often use this capability to safely share customer's financial information with a broker.

Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs) - unlike AISPs, which can only view customers’ financial data, Payment Initiation Service Providers are authorized to handle payments on behalf of a customer.
A few examples of Payment Initiation Service Providers are those financial management tools that automatically transfer a customer’s funds and also those business solutions that allow companies to manage payments and collections better.

Benefits of PSD2 for businesses and customers
The Revised Payment Services Directive enables both customers and merchants to manage their funds more conveniently.
PSD2 will also give e-commerce businesses opportunities to increase the speed of services, build their clientele faster, and improve payment security.
The reviewed PSD will enable Third-Party Providers to build financial services by using the existing banks’ infrastructure.
Very soon, EU bank holders might start using Facebook and Amazon to pay their bills, make money transfers, and analyze their spendings.
Also, with merchants receiving funds directly from a customer, money transfers and card payments are expected to get cheaper and quicker.
The Revised Payment Service Directive (PSD2) has sparked a lot of lively conversations in the fintech industry.
The new Account Information Service Provider model leads a major shift in data aggregation, opening a lot of opportunities for companies that collect data. In simple terms, PSD2 gives fintech businesses the legal tools to build new financial services by using existing banks’ data and services.
Combining the reliability of existing financial structures with the innovative power of startups, this approach will, without a doubt, significantly benefit the market.
Enhanced security is also among the benefits of PSD2. To protect customers from fraud, PSD2 requires financial organizations to implement multi-factor authentication: Knowledge (password, SIN), Possession (token, smart card), Inherence (biodata).
Because the factors selected are mutually independent, the breach of one will not compromise other factors entirely.
It goes without saying, the Revised Directive is leading a major change in the way banking works. The PSD2 promises to promote innovation, provide enhanced security across the board, and encourage competition.



